If you work with dates in SAS, you often need today’s date.
But, how do you get today’s date in SAS? In SAS, both the TODAY() function and the DATE() function give you the current date. These functions will return the number of days between the 1st of January 1960 and today. So, to make them appear as a date, you have to apply a format.
In this article, we demonstrate how you can use these functions.
Contents
Print Today’s Date to the SAS Log
You can use the TODAY() or DATE() function in combination with a _NULL_ dataset to print today’s date to the SAS log.
In the examples below, we show how to generate the current date, apply the most used SAS date formats, and print the result to the log.
Today’s Date in DDMMMYYYY Format
data _null_; my_date = today(); format my_date date9.; put "Current Date (formatted as DDMMMYYYY): " my_date; run;

Today’s Date in MM-DD-YYYY Format
data _null_; my_date = today(); format my_date mmddyyd10.; put "Current Date (formatted as MM-DD-YYYY): " my_date; run;
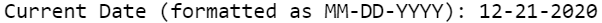
Today’s Date in MM/DD/YYYY Format
data _null_; my_date = today(); format my_date mmddyy10.; put "Current Date (formatted as MM/DD/YYYY): " my_date; run;
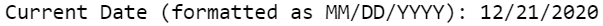
Today’s Date in DD-MM-YYYY Format
data _null_; my_date = today(); format my_date ddmmyyd10.; put "Current Date (formatted as DD-MM-YYYY): " my_date; run;
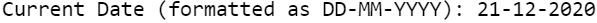
Today’s Date in DD/MM/YYYY Format
data _null_; my_date = today(); format my_date ddmmyy10.; put "Current Date (formatted as DD/MM/YYYY): " my_date; run;
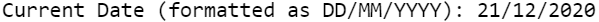
Today’s Date in Worddate Format
data _null_; my_date = today(); format my_date worddate.; put "Current Date: " my_date; run;

Today’s Date in Weekdate Format
data _null_; my_date = today(); format my_date weekdate.; put "Current Date: " my_date; run;
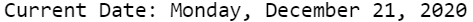
Create a New SAS Variable with Today’s Date
You can also use the TODAY() or DATE() function to create a new SAS variable. For example, with the code below, we create a new SAS dataset with 5 rows where the column date_column contains the current date.
data work.my_ds; do i = 1 to 5; some_text = "Today's date is:"; date_column = today(); output; end; format date_column date9.; drop i; run;
In the example above, we created a new variable with the current date. SAS offers also the MDY() function to create dates. Read this post to learn more about the MDY() function.
For more, general information about creating new variable, read this post.
Use Today’s Date in a SAS Function
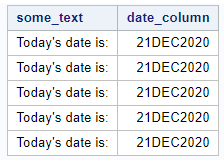
You can also use the TODAY() or DATE() function as part of another function (a so-called nested function). For example, here we calculate the number of days between a given date (i.e., start) and today’s date.
data work.my_ds; start = "01JAN2020"D; today = today(); diff_in_days = intck("day", start, today); output; start = "04FEB2020"D; today = today(); diff_in_days = intck("day", start, today); output; start = "13SEP2020"D; today = today(); diff_in_days = intck("day", start, today); output; start = "01JAN2021"D; today = today(); diff_in_days = intck("day", start, today); output; format start today date9.; run;
In the example above, we used the INTCK() function to calculate the difference between two dates. This isn’t its only functionality. The INTCK() function is a very powerful function with lots of uses. Read our other post to get the most out of this function.
Create a Macro Variable with Today’s Date
User-Defined Macro Variables
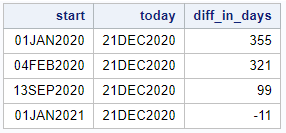
You can also get the current date in a user-defined macro variable. For this, you need to write the TODAY() function within the %SYSFUNC function.
%let my_date_no_format = %sysfunc(today()); %put &=my_date_no_format.;
As the example above shows, the result of the TODAY() function is saved as a macro variable, but it isn’t easily interpretable as a date. So, we need to apply a SAS date format. In the code below, we apply the date9. format to the macro variable with the current date.
%let my_date_formatted = %sysfunc(today(), date9.); %put &=my_date_formatted.;

Do you know? How to Remove a User-Defined Macro Variable
Automatic Macro Variables
Besides used-defined macro variables, SAS has also automatic macro variables that contain the current date (and time). These macro variables always exist and contain the current date (and time) when you use them.
The SYSDATE and SYSDATE9 variables contain today’s date. The only difference between these two automatic macro variables is their format. As the name suggest, the SYSDATE9 contains the current date in the DATE9. format. SYSDATE has the DATE7. format.
Note that, these automatic macro variables are strings. Hence, if you want to use them in a calculation, you need to place them between double quotes and the character “d”.
For example:
data work.my_ds; todays_date = "&sysdate9."; tomorrows_date = intnx("day", "&sysdate9."d, 1); output; format tomorrows_date date9.; run;
There are two other automatic macro variables that you might find useful, namely SYSDAY and SYSTIME. As the name suggest, the SYSDAY macro variable contains today’s day, while SYSTIME has the current time (hours and seconds).
Get the Current Datetime in SAS
You can use the DATETIME function to get the current datetime in SAS. Each time you use this function, SAS returns the value that represents the current date with a timestamp. So, you need to apply a datetime format to make this value easy to interpret.
In the example below we use the DATETIME function to create a new variable with the current date and time.
data _null_; my_datetime = datetime(); format my_datetime datetime20.; put "Current Date Time: " my_datetime; run;
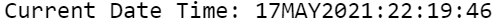
Do you know? How to Convert a SAS Date into a SAS Datetime or Convert a SAS Datetime into a SAS Date


